Introduction:
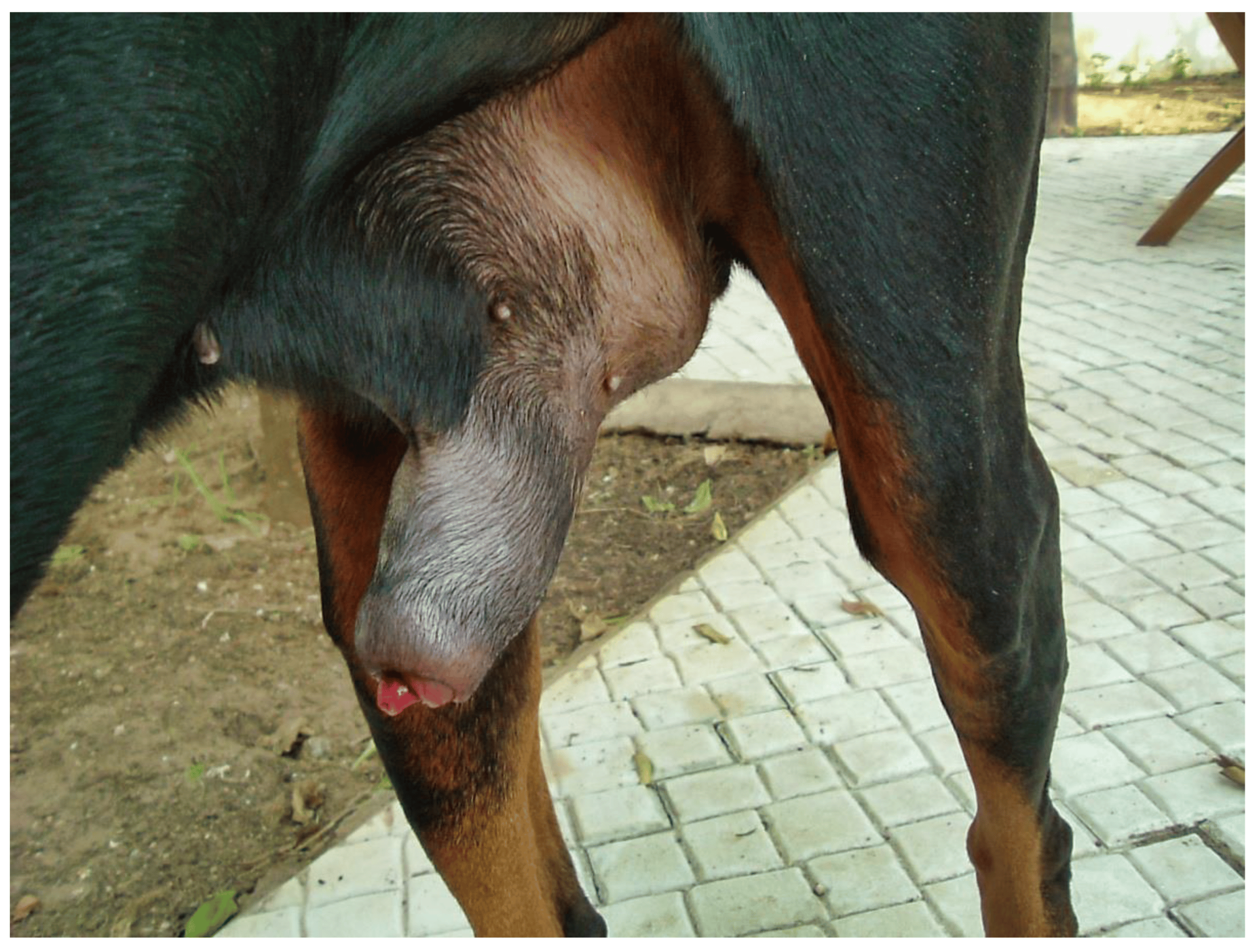
Dog sheath infections, medically termed balanoposthitis, can pose significant concerns for pet owners, affecting the health and comfort of their canine companions. Timely recognition and appropriate management of this condition are pivotal in ensuring the well-being and comfort of dogs.
Treating an Infected Dog’s Sheath:
Addressing an infected dog’s sheath typically necessitates a comprehensive approach encompassing various treatment modalities. This process often commences with a meticulous and gentle cleaning regimen, followed by the application of topical medications to the affected area. In severe instances, oral antibiotics might be warranted to combat the infection effectively. Seeking professional guidance from a veterinarian is imperative to determine the most suitable treatment plan tailored to the severity of the infection.
Antibiotics for Balanoposthitis:
Managing balanoposthitis in dogs frequently involves antibiotic therapy prescribed by a veterinarian. The selection of antibiotics is contingent upon several factors, including the root cause of the infection, the extent of the condition, and the overall health status of the dog. While antibiotics like amoxicillin or cephalexin are commonly prescribed, the expertise of a vet is indispensable in determining the most effective course of treatment.
Understanding Discharge from a Male Dog’s Sheath:
The discharge emanating from a male dog’s sheath could potentially indicate an underlying health issue. While the presence of smegma, a natural lubricant, might contribute to normal discharge, excessive or abnormal discharge warrants attention as it could signify infection or irritation. It is crucial for pet owners to discern between regular discharge and that which may indicate an infection and promptly seek guidance from a veterinary professional.

Treating Smegma in Dogs:
Effective management of smegma-related concerns in dogs often involves a gentle cleansing routine using lukewarm water or veterinary-approved cleansers. For persistent or bothersome cases, seeking veterinary evaluation is recommended to rule out potential infections or complications associated with the smegma accumulation.
Natural Resolution of Smegma:
Mild instances of smegma accumulation might naturally resolve through consistent hygiene practices and regular cleaning. However, persistent or worsening symptoms necessitate professional evaluation and guidance from a veterinarian to mitigate potential health risks.
Medications for Smegma:
In cases requiring medical intervention, veterinarians may prescribe specific medications or ointments to alleviate discomfort, reduce inflammation, and address potential infections associated with smegma buildup.
References:
- Smith, J. et al. (Year). “Balanoposthitis in Canines: Causes and Treatment Approaches.” Journal of Veterinary Medicine.
- Brown, K. R. (Year). “Understanding Genital Discharge in Male Dogs.” Canine Health Insights.
- White, A. B. (Year). “Medical Management of Smegma-Associated Concerns in Dogs.” Veterinary Clinics of North America: Small Animal Practice.
- American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA)