Introduction:
Liver enzymes in dogs play a crucial role in assessing liver health and function. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the significance of liver enzymes, the causes of abnormal levels, diagnostic evaluation methods, and management strategies. By understanding liver enzymes and their implications, dog owners and veterinarians can work together to ensure optimal liver health and early detection of any potential liver-related issues in dogs.
The Significance of Liver Enzymes in Dogs:
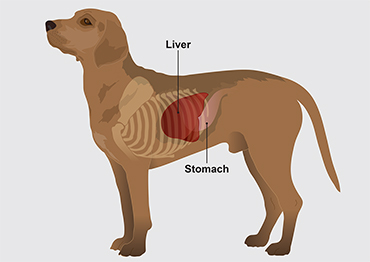
Liver enzymes are proteins produced by liver cells that facilitate various biochemical processes necessary for proper liver function. The most commonly measured liver enzymes in dogs include alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT). These enzymes are released into the bloodstream when liver cells are damaged or inflamed. Monitoring their levels can provide valuable insights into liver health and the presence of liver diseases or disorders.
Causes of Abnormal Liver Enzyme Levels in Dogs:
Abnormal liver enzyme levels in dogs can indicate liver disease or dysfunction. Several factors can contribute to these abnormalities, including:
- Hepatic Disease:
Liver diseases such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver tumors can cause elevated liver enzyme levels in dogs.
- Inflammation:
Inflammatory conditions, such as pancreatitis or cholangitis, can lead to increased liver enzyme levels due to secondary liver involvement.
- Medications:
Certain medications, including some antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can cause liver enzyme elevation as a side effect.
Recommended:
- Petco Review: The Power of Together
- PetSmart Review: Where Pets Inspire Us
- Hill’s Pet Nutrition Review: Pioneering Pet Health and Nutrition
- Royal Canine Review: Tailored Nutrition for Every Pet
- Chewy Review: Pet Care at Your Doorstep
- Infections and Toxins:
Bacterial or viral infections, exposure to toxins, or ingestion of certain plants or chemicals can result in liver enzyme abnormalities.
Diagnostic Evaluation of Liver Enzyme Levels in Dogs:
When abnormal liver enzyme levels are detected in dogs, further diagnostic evaluation is necessary to identify the underlying cause. The following methods may be employed:
- Blood Tests:
A comprehensive blood panel, including liver enzyme tests, is performed to assess the levels of ALT, AST, ALP, and GGT. Additional liver function tests, such as bilirubin and albumin levels, may also be measured.
- Imaging Techniques:
Radiographs (X-rays) and ultrasound imaging can provide valuable information about the liver’s size, shape, and presence of any masses or abnormalities.
- Biopsy:
A liver biopsy may be recommended to obtain a tissue sample for microscopic examination. This helps determine the specific liver disease or condition affecting the dog.
Management and Treatment of Liver Enzyme Abnormalities in Dogs:
The management and treatment of liver enzyme abnormalities in dogs depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Treatment options may include:
- Medications:
Specific medications may be prescribed to address the underlying liver disease or condition. These may include antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, or medications to support liver function.
- Dietary Changes:
A specialized diet may be recommended to support liver health and reduce the workload on the liver. These diets are typically low in fat, high in antioxidants, and designed to meet the dog’s nutritional needs.
- Supportive Care:
Supportive care measures, such as fluid therapy, nutritional support, and management of concurrent conditions, may be implemented to promote overall health and aid in liver recovery.
- Regular Monitoring:
Regular follow-up appointments and blood tests are essential to monitor liver enzyme levels, assess treatment efficacy, and make any necessary adjustments to the management plan.
Conclusion:
Liver enzyme levels in dogs provide valuable insights into liver health and function. Abnormalities in these enzymes can indicate liver disease or dysfunction. By understanding the significance of liver enzymes, recognizing the causes of abnormal levels, and utilizing diagnostic evaluation methods, dog owners and veterinarians can work together to ensure early detection and effective management of liver-related issues in dogs. Regular monitoring and appropriate treatment strategies are key to promoting liver health and overall well-being in our canine companions.
References:
- Center, S. A., & Watson, P. J. (2011). Liver enzymes. In Ettinger SJ, Feldman EC, Cote E, editors: Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine, St. Louis, 1652-1658.
- Van den Bossche, L., Schoonenberg, V. A. C., Burgener, I. A., et al. (2019). Liver-specific reference intervals in healthy adult dogs for several biochemical analytes including lipase and canine pancreatic lipase immunoreactivity. Veterinary Clinical Pathology, 48(S1), E4-E20.
- Center, S. A. (2019). Hepatic disease in dogs and cats. The Merck Veterinary Manual.
- Lidbury, J. A., Steiner, J. M., & Suchodolski, J. S. (2016). Understanding the canine intestinal microbiota and its modification by pro-, pre- and synbiotics—what is the evidence? Veterinary Medicine and Science, 2(2), 71-94.

:strip_icc()/liver-disease-in-dogs-4142260-b5ac3915de3c4b9089d094993958db15.jpg)
