Cat bacterial infection is a common health issue that affects feline companions worldwide. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of cat bacterial infections, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies. Understanding these aspects is crucial for cat owners and veterinarians to ensure the well-being and longevity of their feline friends.
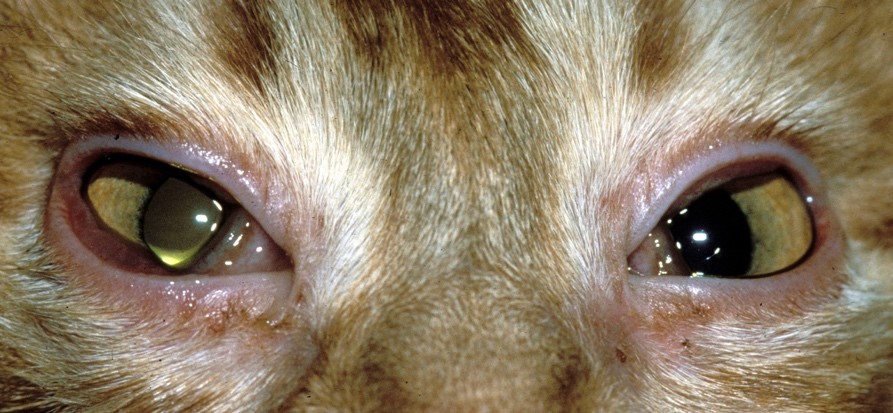
Bacterial infections in cats can be caused by a variety of pathogens, including bacteria such as Pasteurella multocida, Bartonella henselae, and Staphylococcus aureus. These infections can affect different body systems, including the respiratory, urinary, gastrointestinal, and integumentary systems. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential to prevent complications and promote a speedy recovery.
Causes of Cat Bacterial Infections:
Cat bacterial infections can be acquired through various means. One common route of transmission is through direct contact with infected animals. Cats that roam freely and come into contact with other cats, wildlife, or even humans are at a higher risk. Additionally, bites from fleas, ticks, or other parasites can introduce bacteria into a cat’s system, leading to infection. Poor hygiene, crowded living conditions, and a weakened immune system can also increase a cat’s susceptibility to bacterial infections.
Recommended:
- Petco Review: The Power of Together
- PetSmart Review: Where Pets Inspire Us
- Hill’s Pet Nutrition Review: Pioneering Pet Health and Nutrition
- Royal Canine Review: Tailored Nutrition for Every Pet
- Chewy Review: Pet Care at Your Doorstep
Symptoms of Cat Bacterial Infections:
The symptoms of cat bacterial infections can vary depending on the specific bacteria involved and the affected body system. However, some common signs to watch out for include:
-
Respiratory Infections:
– Sneezing
– Coughing
– Nasal discharge
– Difficulty breathing
-
Urinary Tract Infections:
– Frequent urination
– Blood in urine
– Straining to urinate
– Urinating outside the litter box
-
Gastrointestinal Infections:
– Vomiting
– Diarrhea
– Loss of appetite
– Abdominal pain
-
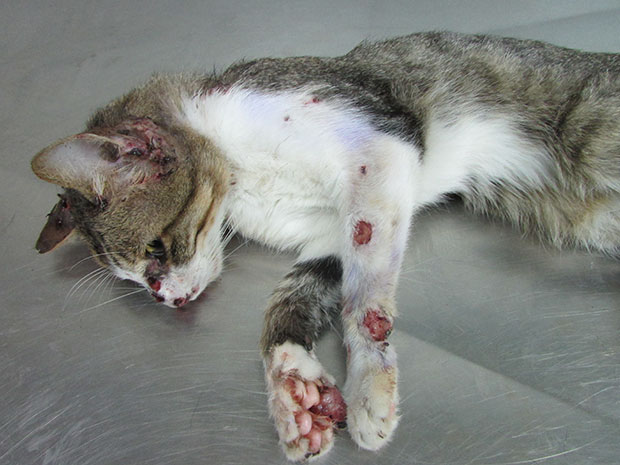
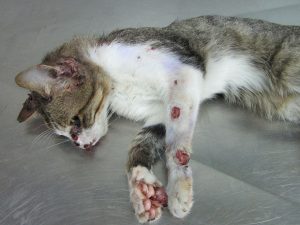
Skin Infections:
– Redness and inflammation
– Itching and scratching
– Hair loss
– Presence of sores or abscesses
Diagnosis of Cat Bacterial Infections:
To diagnose a bacterial infection in cats, veterinarians may perform various tests, including physical examinations, blood work, urine analysis, and culture and sensitivity tests. These tests help identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and determine the most effective treatment options. In some cases, imaging techniques such as X-rays or ultrasounds may be necessary to assess the extent of the infection or identify any underlying conditions.
Treatment of Cat Bacterial Infections:
The treatment of cat bacterial infections typically involves a combination of medication, supportive care, and addressing any underlying health issues. Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to target the specific bacteria causing the infection. The duration of treatment may vary depending on the severity of the infection and the response to medication. It is crucial to follow the veterinarian’s instructions regarding dosage and administration to ensure effective treatment and prevent the development of antibiotic resistance.
Supportive care measures, such as providing a comfortable and stress-free environment, ensuring proper nutrition, and administering fluids if necessary, can help boost the cat’s immune system and aid in the recovery process. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required for close monitoring and intensive treatment.
Prevention of Cat Bacterial Infections:
Preventing cat bacterial infections involves a combination of proactive measures and regular veterinary care. Here are some essential preventive strategies:
- Vaccination: Ensure your cat is up to date with vaccinations to protect against common bacterial infections, such as feline respiratory diseases and feline leukemia.
- Parasite Control: Regularly use flea and tick preventives to reduce the risk of bacterial transmission through bites.
- Hygiene: Maintain good hygiene practices by regularly cleaning litter boxes, providing clean water and food bowls, and grooming your cat to minimize the risk of skin infections.
- Stress Reduction: Minimize stress in your cat’s environment, as stress can weaken the immune system and make cats more susceptible to infections.
- Regular Veterinary Check-ups: Schedule routine check-ups with your veterinarian to detect any potential health issues early on and address them promptly.
Conclusion:
Cat bacterial infections can significantly impact a cat’s health and well-being if left untreated. Prompt diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and preventive measures are essential for managing these infections effectively. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies discussed in this article, cat owners and veterinarians can work together to ensure the best possible care for their feline companions.
References:
- Smith, B. P. (2015). Large Animal Internal Medicine. Elsevier Health Sciences.
- Little, S. E. (2010). Bartonella spp. infection as a model of emerging infectious diseases. Clinical microbiology reviews, 23(3), 545-558.